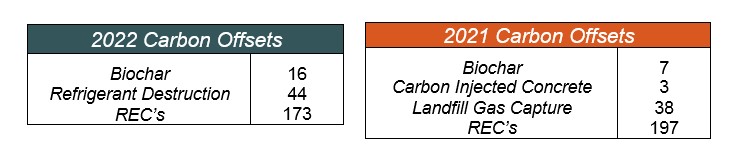
In terms of diversification, while continuing to support permanent removal projects with strong additional attributes in the form of biochar credits, Spirit purchased refrigerant emissions avoidance credits in recognition of the continued impact of these sources, especially in developing countries. Since those refrigerants are so harmful from a climate perspective and the programs to collect and safely dispose of them are relatively affordable, these credits are also quite economical on a per metric ton of CO2e basis. Refrigerant credits support products containing refrigerants that have been banned in North America since the Montreal Protocol. This allows them to be safely disposed of rather than being landfilled where the risk of puncture and gas release is much higher. Although less common in the United States, carbon pollution is global, and the net impact is the same.
By adjusting the ratio of refrigerant credits purchased to biochar credits purchased, Spirit was able to buy offsets for a marginal increase in per credit cost (roughly $21/credit). This allowed Spirit to both address a timely issue of keeping these high impact GHGs from entering the atmosphere while keeping costs lower and providing a better carbon return on investment(cROI). As a result, Spirit was able to continue to cover the higher output of commuting emissions for team members and keep more money on hand to invest back in the business.
Spirit avoided Scope 2 emissions by voluntarily purchasing Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) for the Texas office’s electricity use and the Denver office’s electricity before relocating to a carbon neutral building; Spirit’s office in Denver is now located in the Alliance Center, where all Scope 2 emissions are offset. The cost of RECs purchased for 2022 emissions did increase from 2021 by approximately 18%, which was deemed acceptable based on average market costs.
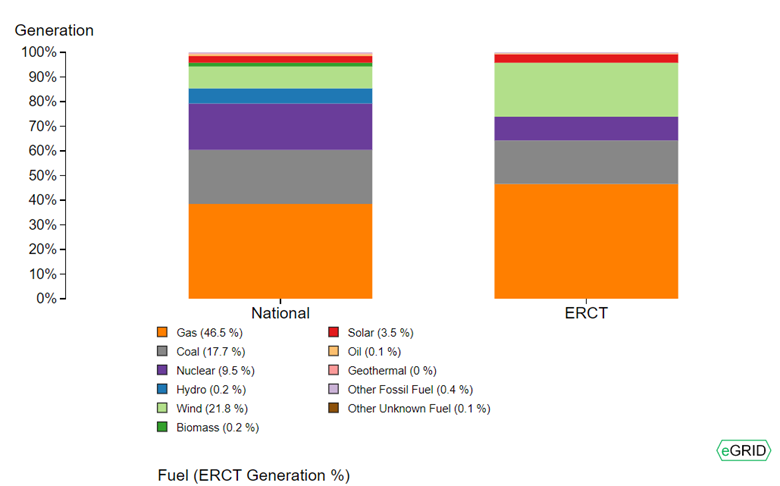
RECs are sold as the cost associated with generating 1 MWh of carbon free energy. By purchasing RECs equal to the amount of Spirit’s electricty consumption in Texas, the amount of renewable and low carbon energy in the Texas ERCT subregion energy portfolio (about 26% renewables in wind, solar, biomass and hydro, and 9.5% low carbon in nuclear per the graphic below) is not considered, resulting net renewable generation per MWh consumed of more than 1 MWh of clean energy. However, since the RECs associated with the renewable energy on the grid in Texas are not conveyed to Spirit and may be sold otherwise as part of a green power program or to meet compliance targets, Spirit has no claim to the relatively high percentage of low and no carbon electricity consumed without buying RECs.